
Your organization must prepare for possible risks when engaging with stakeholder groups. It is important to identify your stakeholders and how they will participate. You have many options for completing this risk assessment. For instance, you can use a stakeholder engagement matrix to identify key stakeholders and identify their authority and response capabilities.
Stakeholder engagement matrix
The stakeholder matrix for engagement helps identify the current level and desired level of engagement. The matrix is also useful in understanding the relationships between different stakeholder group. The stakeholder engagement matrix is useful for project managers in helping them to understand the interests and importance of different stakeholder groups.
First, identify all stakeholders. The stakeholder engagement matrix allows the project team to determine whether a stakeholder supports, opposes, or is neutral about a project. Once the stakeholders are identified, it is possible for the project team to analyze the reasons for their engagement. If a stakeholder has expressed negative opinions regarding a project the team would prefer to work first with this group before working with other stakeholders.
Stakeholder identification
The identification and engagement of stakeholders is critical for the conduct and review of a project. However, it can be difficult to know who should be involved. The EviEM process identifies stakeholders at two levels, including the broader community and specific groups with different interests. This approach provides two distinct benefits.
The first step to engaging stakeholder engagement is stakeholder analysis. This analysis will identify the stakeholder category and the desired level of engagement for each group. From there, a strategy is developed for each individual stakeholder.
Stakeholder response development
An assessment of stakeholder response risk involves identifying possible risks and assessing the likelihood that they will occur. The risk assessment must assess the probability and severity of risks and their potential impact on the project's objectives, budget, deliverables, and financial resources. It should also include an action plan for dealing with the risks. However, the response plan doesn't necessarily need to be immediate.
Stakeholders are groups of people who will be impacted by a project and have the potential for influence. Stakeholders need to have an interest in the project and special skills that could make or break it. They must be able and willing to change.
Stakeholder authority
It is important to determine the authority of each stakeholder before implementing a project. The project managers will be able to determine how best to work with each stakeholder by knowing their intentions and power. The chances of a project's success can be increased by working with both supporters and opponents. This article will provide some tips and tricks for planning stakeholder involvement.
It is important to know how each stakeholder views risk. Different people will view risk differently. This is particularly important when stakeholders feel they play a significant role in decision making.
Communication strategy
Communication with stakeholders is essential to the stakeholder engagement risk evaluation process. For a communication strategy to be successful, organizations need first to understand the needs and expectations their stakeholders. These are the steps you need to take in order to plan stakeholder engagement communication risk assessment: Identify your stakeholders
2. Create and implement a communication plan. Your stakeholders' interests, influence levels, and feedback methods should all be considered when you design and implement a communication strategy. It should be flexible enough that it can accommodate the priorities and needs of each stakeholder group.
FAQ
Why does it sometimes seem so difficult to make good business decisions?
Complex systems with many moving parts are the hallmark of businesses. They require people to manage multiple priorities and deal with uncertainty and complexity.
Understanding the impact of these factors on the system is crucial to making sound decisions.
This requires you to think about the purpose and function of each component. It is important to then consider how the individual pieces relate to each other.
Ask yourself if there are hidden assumptions that have influenced your behavior. If not, you might want to revisit them.
Asking for assistance from someone else is a good idea if you are still having trouble. You may be able to see things from a different perspective than you are and gain insight that can help you find a solution.
What are some common management mistakes?
Sometimes managers make it harder for their employees than is necessary.
They may not delegate enough responsibilities to staff and fail to give them adequate support.
Managers often lack the communication skills necessary to motivate and guide their teams.
Managers can set unrealistic expectations for their employees.
Managers may prefer to solve every problem for themselves than to delegate responsibility.
How does a manager motivate his/her employees?
Motivation is the desire for success.
It is possible to be motivated by doing something you enjoy.
You can also be motivated by the idea of making a difference to the success and growth of your organization.
If you are a doctor and want to be one, it will likely be more rewarding to see patients than to read medical books every day.
The inner motivation is another type.
For example, you might have a strong sense of responsibility to help others.
Perhaps you enjoy working hard.
Ask yourself why you aren't feeling motivated.
You can then think of ways to improve your motivation.
What is a fundamental management tool for decision-making?
A decision matrix is a simple but powerful tool for helping managers make decisions. It allows them to consider all possible solutions.
A decision matrix is a way to organize alternatives into rows and columns. This makes it easy to see how each alternative affects other choices.
We have four options in this example. They are represented by the boxes to the left of the matrix. Each box represents one option. The top row shows the status quo (the current situation), and the bottom row shows what would happen if nothing was done at all.
The middle column displays the impact of selecting Option 1. In this example, it would lead to an increase in sales of between $2 million and $3 million.
The following columns illustrate the impact of Options 2 and 3. These are good changes, they increase sales by $1million or $500,000. They also have negative consequences. Option 2 increases the cost of goods by $100,000. Option 3 decreases profits and makes them less attractive by $200,000.
The final column shows the results for Option 4. This will result in sales falling by $1,000,000
The best part of using a decision-matrix is that it doesn't require you to know which numbers belong where. You just look at the cells and know immediately whether any given a choice is better than another.
This is because the matrix has already taken care of the hard work for you. It's simply a matter of comparing the numbers in the relevant cells.
Here's a sample of how you might use decision matrixes in your business.
Decide whether you want to invest more in advertising. If you do, you'll be able to increase your revenue by $5 thousand per month. You'll also have additional expenses up to $10,000.
Look at the cell immediately below the one that states "Advertising" to calculate the net investment in advertising. It's $15,000. Advertising is more valuable than its costs.
Statistics
- The BLS says that financial services jobs like banking are expected to grow 4% by 2030, about as fast as the national average. (wgu.edu)
- As of 2020, personal bankers or tellers make an average of $32,620 per year, according to the BLS. (wgu.edu)
- Our program is 100% engineered for your success. (online.uc.edu)
- The profession is expected to grow 7% by 2028, a bit faster than the national average. (wgu.edu)
- Your choice in Step 5 may very likely be the same or similar to the alternative you placed at the top of your list at the end of Step 4. (umassd.edu)
External Links
How To
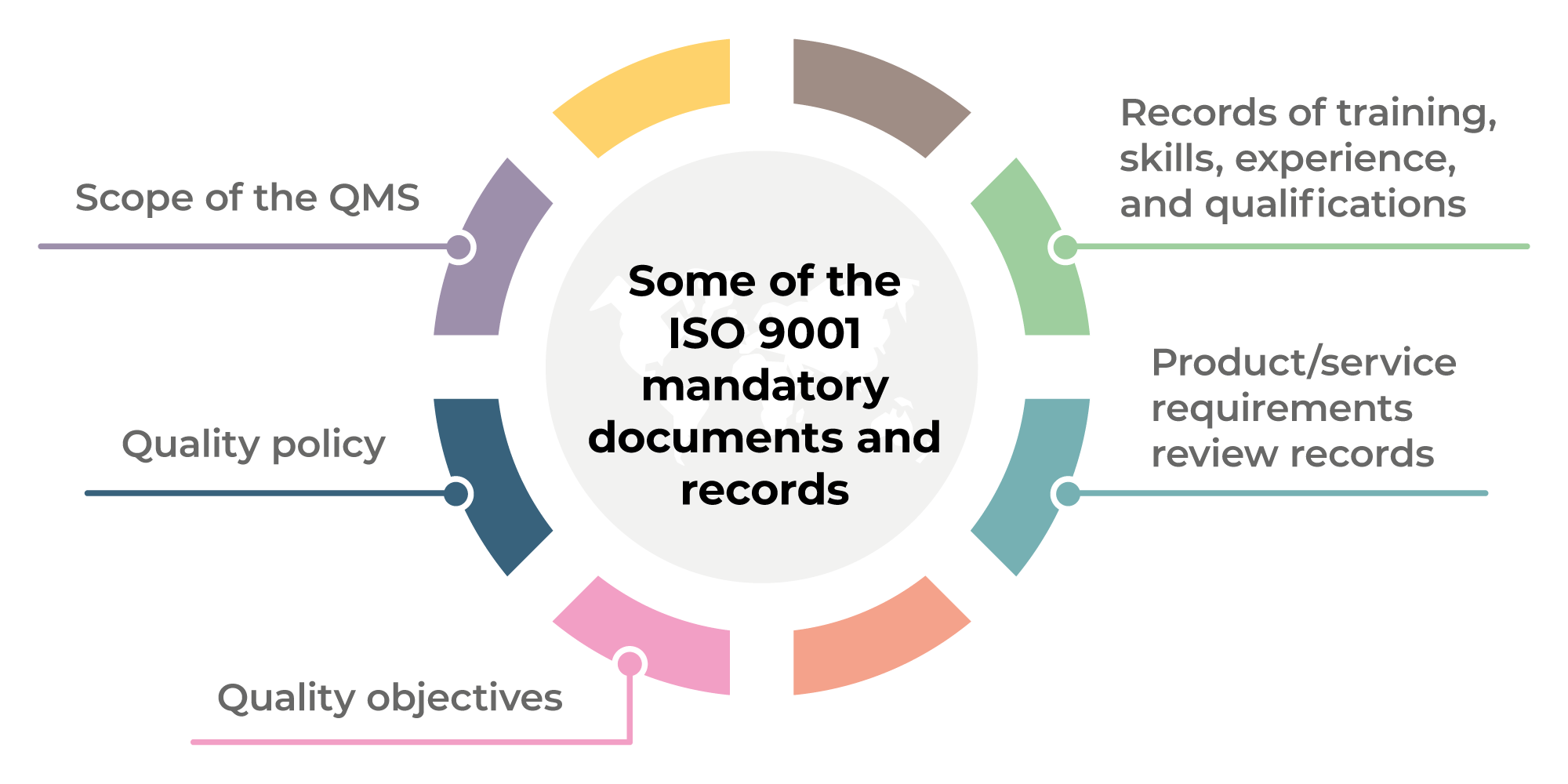
How can you create a Quality Management Plan, (QMP)?
The Quality Management Plan (QMP) was established in ISO 9001. It is a systematic way to improve processes, products and services. It provides a systematic approach to improving processes, products and customer satisfaction by continuously measuring, analysing, controlling, controlling, and improving them.
QMP is a standard way to improve business performance. QMP helps improve production, service delivery and customer relationships. QMPs should encompass all three components - Products and Services, as well as Processes. The QMP that only addresses one aspect of the process is called a Process QMP. If the QMP is focused on a product/service, it's called a QMP. QMP is also used to refer to QMPs that focus on customer relations.
Scope, Strategy and the Implementation of a QMP are the two major elements. They can be described as follows:
Scope: This defines what the QMP will cover and its duration. This will be used to define activities that are performed in the first six months of a QMP.
Strategy: This describes how you will achieve the goals in your scope.
A typical QMP includes five phases: Design, Planning, Development and Implementation. Each phase is explained below:
Planning: This stage determines the QMP goals and prioritizes them. Every stakeholder involved in the project is consulted to determine their expectations and needs. After identifying the objectives, priorities, and stakeholder involvement, the next step is to develop the strategy for achieving these objectives.
Design: This stage is where the design team creates the vision, mission and strategies necessary for successful implementation of QMP. These strategies are implemented by the development of detailed plans and procedures.
Development: Here the development team works toward building the necessary resources and capabilities to support the successful implementation.
Implementation involves the actual implementation using the planned strategies.
Maintenance: This is an ongoing procedure to keep the QMP in good condition over time.
Additional items must be included in QMP.
Stakeholder Involvement: Stakeholders are important for the success of the QMP. They must be involved in all phases of the QMP's development, planning, execution, maintenance, and design.
Project Initiation. It is important to understand the problem and the solution in order to initiate any project. Also, the initiator should understand why they are doing it and what they expect.
Time Frame: It is important to consider the QMP's time frame. If you plan to implement the QMP for a short period, you can start with a simple version. For a long-term commitment you may need more complicated versions.
Cost Estimation - Cost estimation is an important part of the QMP. You cannot plan without knowing how much money you will spend. Before you start the QMP, it is important to estimate your costs.
QMPs are more than just documents. They can also be updated as needed. It changes with the company. It should be reviewed regularly to ensure that it meets current needs.